1. Cross-site scripting (reflected)

2. Password field with autocomplete enabled
3. Cross-domain Referer leakage
4. Cross-domain script include
5. HTML does not specify charset
| Severity: | High |
| Confidence: | Certain |
| Host: | https://secure.comodo.com |
| Path: | /home/purchase.php |
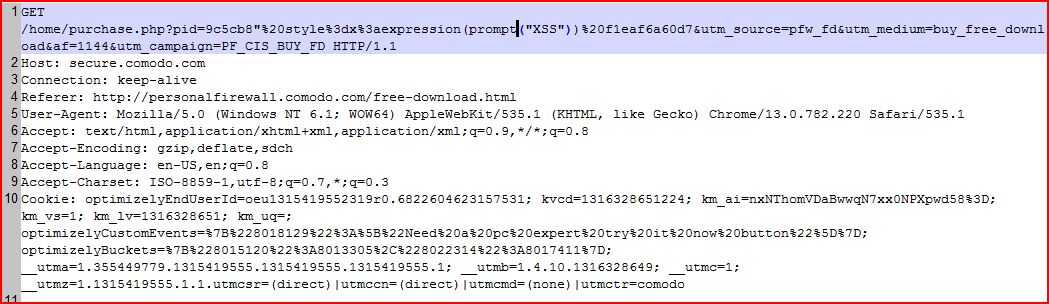
| GET /home/purchase.php?pid=9c5cb8"%20style%3dx Host: secure.comodo.com Connection: keep-alive Referer: http://personalfirewall User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/535.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/13.0.782.220 Safari/535.1 Accept: text/html,application Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate,sdch Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.8 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,* Cookie: optimizelyEndUserId |
| HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: nginx Date: Sun, 18 Sep 2011 01:51:42 GMT Content-Type: text/html Connection: keep-alive Keep-Alive: timeout=5 Vary: Accept-Encoding Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0 Pragma: no-cache Content-Length: 43034 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org <head> <script src="//cdn.opti ...[SNIP]... <a href="includes/video.php ...[SNIP]... |
| Severity: | Low |
| Confidence: | Certain |
| Host: | https://secure.comodo.com |
| Path: | /home/purchase.php |
| GET /home/purchase.php?pid=9 Host: secure.comodo.com Connection: keep-alive Referer: http://personalfirewall User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/535.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/13.0.782.220 Safari/535.1 Accept: text/html,application Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate,sdch Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.8 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,* Cookie: optimizelyEndUserId |
| HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: nginx Date: Sun, 18 Sep 2011 01:50:26 GMT Content-Type: text/html Connection: keep-alive Keep-Alive: timeout=5 Vary: Accept-Encoding Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0 Pragma: no-cache Content-Length: 42824 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org <head> <script src="//cdn.opti ...[SNIP]... </h1> <form name="select-product" method="post" action="order.php"> <div class="top-error"> ...[SNIP]... <td colspan="2"><input type="password" id="password" name="password" value="" /></td> ...[SNIP]... <td colspan="2"><input type="password" id="verify_password" name="verify_password" value="" /></td> ...[SNIP]... <input type="hidden" id="cc_cvv" name="cc_cvv" value="ab8d81f3c06b6 <input type="password" maxlength="4" id="ab8d81f3c06b6c3f </td> ...[SNIP]... |
| Severity: | Information |
| Confidence: | Certain |
| Host: | https://secure.comodo.com |
| Path: | /home/purchase.php |
| GET /home/purchase.php?pid=9 Host: secure.comodo.com Connection: keep-alive Referer: http://personalfirewall User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/535.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/13.0.782.220 Safari/535.1 Accept: text/html,application Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate,sdch Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.8 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,* Cookie: optimizelyEndUserId |
| HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: nginx Date: Sun, 18 Sep 2011 01:50:26 GMT Content-Type: text/html Connection: keep-alive Keep-Alive: timeout=5 Vary: Accept-Encoding Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0 Pragma: no-cache Content-Length: 42824 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org <head> <script src="//cdn.optimizely.com ...[SNIP]... </script> <script type="text/javascript" src="https://www </script> ...[SNIP]... <div style="display:inline;"> <img height="1" width="1" style="border-style:none; </div> ...[SNIP]... |
| Severity: | Information |
| Confidence: | Certain |
| Host: | https://secure.comodo.com |
| Path: | /home/purchase.php |
| GET /home/purchase.php?pid=9 Host: secure.comodo.com Connection: keep-alive Referer: http://personalfirewall User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/535.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/13.0.782.220 Safari/535.1 Accept: text/html,application Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate,sdch Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.8 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,* Cookie: optimizelyEndUserId |
| HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: nginx Date: Sun, 18 Sep 2011 01:50:26 GMT Content-Type: text/html Connection: keep-alive Keep-Alive: timeout=5 Vary: Accept-Encoding Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0 Pragma: no-cache Content-Length: 42824 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org <head> <script src="//cdn.optimizely.com ...[SNIP]... </script> <script type="text/javascript" src="https://www </script> ...[SNIP]... |
| Severity: | Information |
| Confidence: | Certain |
| Host: | https://secure.comodo.com |
| Path: | /home/images/CIS5.jpg |
| GET /home/images/CIS5.jpg HTTP/1.1 Host: secure.comodo.com Connection: keep-alive Referer: https://secure.comodo.com User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/535.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/13.0.782.220 Safari/535.1 Accept: */* Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate,sdch Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.8 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,* Cookie: optimizelyEndUserId |
| HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found Server: nginx Date: Sun, 18 Sep 2011 01:50:32 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 564 Connection: keep-alive Keep-Alive: timeout=5 <html> <head><title>404 Not Found</title></head> <body bgcolor="white"> <center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center> <hr><center>nginx</center </body> </html> <!-- a padding to disable MSIE and Chr ...[SNIP]... |